Major
components of Automobile
1.
Basic
structure
2.
Power plant
3.
Transmission
system
4.
Auxiliaries
5.
Controls
1)
Basic structure- This is
nothing but a unit on which the remaining units are required to be mounted. It
consists of- frame, suspension system, axles, wheels, and tires.
1.1Frame-
It is generally a steel structure to which all
mechanical units are attached and on which the body is superimposed.
Location- Frame is
the most supportive part of an automobile and fixed at the bottom.
1.2Suspension
system-
It prevents vehicle
components and occupants (passengers) from road shocks. It maintains the
stability of the vehicle in dynamic conditions.
Location- This system
is situated dependently or independently near the wheels.
1.3Axles-
As the axles
are weight carrying elements, they are considered as supported beams. Axles are
normally carrying a vertical load, torque reactions, side thrust, etc.
Location- Axles are
bonding two wheels together indirectly hence located at the lower side near
wheels.
1.4Wheels and
tires-
The basic purpose
of wheels and tires is to provide the ride with safety. Generally, natural
rubber is the main component in tire manufacturing.
Location- The part of
the vehicle which comes in direct contact with the road surface is tire. And tire
is like a cover to wheels. Wheels are located at the endpoints of axles.
2)
Power plant- Engine is the power
plant of an automobile. Basically, the engine provides motive power to the
various components of an automobile. This motive power will ultimately drive
the vehicle. The most promising future power plant is the one based on fuel
cells, which would give zero-emission vehicles.
Location-
Power plant (engine) is mounted on a chassis at the frontal side (generally) of
vehicle.
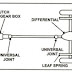
3)
Transmission system- It consists
of the clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, universal joints, differential, axles
etc.
Functions-
i)
to disconnect the engine from the road wheels
whenever required
ii)
to connect the engine to the driving wheels
without shocks
iii)
to turn the drive through 90 degrees
Location- Transmission
the line starts from the clutch and ends up with differential. Generally, it is
situated at the bottom side of an automobile.
4)
Auxiliaries- All electrical systems
in an automobile are collectively called as auxiliaries. It consists of mainly-
Battery, generator, starter, electrical ignition system, lighting system, music system, etc.
Location- Electric
ignition system is fixed at engine side while music system is the part of
vehicle interior.
5)
Controls- Steering system and
brakes are two controlling units of an automobile. The steering provides
directional stability while braking contributes to safety.
Location- Steering system
is located at the frontal side while the braking system is at wheels.